Apatinib
[N-[4-(1-cyano-cyclopentyl)phenyl]-2-(4-pyridylmethyl)amino-3-pyridine
carboxamide] is an orally available, selective small molecule inhibitor of
vascular endothelial growth factor-2 (VEGFR-2 also known as KDR) tyrosine
kinase. It is more potent than Sunitinib in inhibiting VEGFR2 (IC50
Apatinib, Sunitinib = 0.001, 0.005 uM) [1, 2].
Apatinib is an analogue of Valatinib and shows similar anti-angiogenic/anti-tumour efficacy. It binds with VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase targeting the intracellular ATP binding site of the receptor, preventing phosphorylation and subsequent downstream signalling. Apatinib has shown a superior in vivo efficacy compared to Valatinib in xenograft models.
Apatinib has been approved by the Chinese Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) in October 2014 for the treatment of metastatic gastric carcinoma. It is an investigational cancer drug in many other countries including USA, EU etc and currently undergoing clinical trials as a potential targeted treatment for metastatic gastric carcinoma, metastatic breast cancer and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
Apatinib is an analogue of Valatinib and shows similar anti-angiogenic/anti-tumour efficacy. It binds with VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase targeting the intracellular ATP binding site of the receptor, preventing phosphorylation and subsequent downstream signalling. Apatinib has shown a superior in vivo efficacy compared to Valatinib in xenograft models.
Apatinib has been approved by the Chinese Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) in October 2014 for the treatment of metastatic gastric carcinoma. It is an investigational cancer drug in many other countries including USA, EU etc and currently undergoing clinical trials as a potential targeted treatment for metastatic gastric carcinoma, metastatic breast cancer and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
 |
| Apatinib: 2D and 3D Structure |
Angiogenesis, Tumor Angiogenesis and VEGFRs
Angiogenesis,
the formation of new blood vessels from pre-existing ones, plays a central role
in the process of tumor growth and metastasis. The proliferation of endothelium
and formation of new blood vessels further the size of solid tumors. It is
expected that blocking angiogenesis will be an efficient therapeutic approach
against many tumor types.
Tumor angiogenesis plays a critical role in the malignant tumor growth and metastasis. When tumors grow beyond 1 mm3, angiogenesis or generation of vascular arborizations by budding from existing vessels is necessary to provide enough blood for the survival of tumor cells. The growth speed and tendency of metastasis of tumors are associated with the level of neovascularization factors and the quantity of nascent microvessels. Since the hypothesis “anti-angiogenesis therapy” was put forward by Folkman in early 1970s, people have made considerable progress in this field, and inhibiting angiogenesis of tumors has been universally accepted as a new anticancer strategy.
Tyrosine kinase vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor (VEGFR) play significantly important roles in angiogenesis of tumors, and they are both important targets in blocking angiogenesis of tumors. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is the foremost factor in vivo promoting the angiogenesis. The binding of VEGF with vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) in endothelial cells leads to various reactions of angiogenesis, such as cells proliferation, cells metastasis, the increase of vascular permeability, and the move of endothelial cells precursors out of marrow. VEGFR family comprises VEGFR1 (Flt-1), VEGFR2 (KDR/Flk-1) and VEGFR3 (Flt-4). Promotion of the angiogenesis is mainly mediated by the bonded VEGF and VEGFR2 (KDR/Flk-1).
Compared with traditional cytotoxic drugs which inhibit the growth of tumors, angiogenesis targeting drugs are more specific and less toxic as well as helpful to overcome the drug resistance of tumors and can be used for the treatment of various tumors [3, 4].
Tumor angiogenesis plays a critical role in the malignant tumor growth and metastasis. When tumors grow beyond 1 mm3, angiogenesis or generation of vascular arborizations by budding from existing vessels is necessary to provide enough blood for the survival of tumor cells. The growth speed and tendency of metastasis of tumors are associated with the level of neovascularization factors and the quantity of nascent microvessels. Since the hypothesis “anti-angiogenesis therapy” was put forward by Folkman in early 1970s, people have made considerable progress in this field, and inhibiting angiogenesis of tumors has been universally accepted as a new anticancer strategy.
Tyrosine kinase vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor (VEGFR) play significantly important roles in angiogenesis of tumors, and they are both important targets in blocking angiogenesis of tumors. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is the foremost factor in vivo promoting the angiogenesis. The binding of VEGF with vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) in endothelial cells leads to various reactions of angiogenesis, such as cells proliferation, cells metastasis, the increase of vascular permeability, and the move of endothelial cells precursors out of marrow. VEGFR family comprises VEGFR1 (Flt-1), VEGFR2 (KDR/Flk-1) and VEGFR3 (Flt-4). Promotion of the angiogenesis is mainly mediated by the bonded VEGF and VEGFR2 (KDR/Flk-1).
Compared with traditional cytotoxic drugs which inhibit the growth of tumors, angiogenesis targeting drugs are more specific and less toxic as well as helpful to overcome the drug resistance of tumors and can be used for the treatment of various tumors [3, 4].
Apatinib as Kinase Inhibitor
In vitro enzyme experiments showed that Apatinib
was an even more selective inhibitor of VEGFR-2 than Sunitinib, with an IC50
of 0.001 uM and 0.005 uM, respectively. Apatinib could also potently suppress
the activities of Ret, c-Kit and c-Src with an IC50 of 0.013 uM,
0.429 uM and 0.53 uM, respectively. Apatinib had no significant effects on
EGFR, Her-2 or FGFR1 in concentrations up to 10 uM [1].
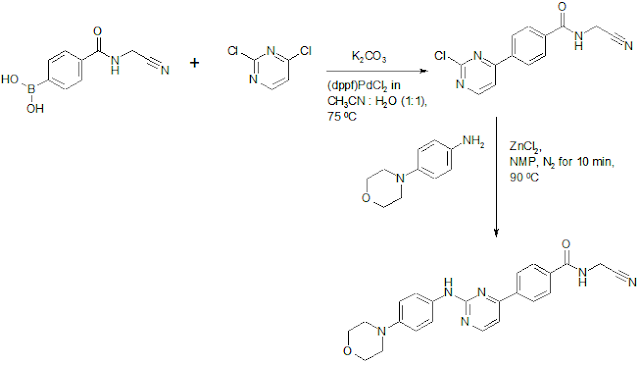
US20040259916A1: It appears to be the industrial process.
Identification:
References:
1. Tian, S.; et al. YN968D1 is a novel and selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase with potent activity in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci 2011, 102(7), 1374-80. (FMO only)
2. Chen, G. Six membered amino-amide derivatives an angiogenisis inhibitors. US20040259916A1
3. Yuan, K.; et al. The salts of n-[4-(1-cyanocyclopentyl)phenyl]-2-(4-pyridyl methyl)amino-3-pyridinecarboxamide. WO2010031266A1
4. Sharma, P. S.; et al. VEGF/VEGFR pathway inhibitors as anti-angiogenic agents: present and future. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2011, 11(5), 624-53. (FMO only)
Summary
Common name: YN968D1; YN 968D1; YN-968D1
Trademarks: -
Molecular Formula: C24H23N5O
CAS Registry Number: 811803-05-1; 1218779-75-9
(mesylate)
CAS Name: N-[4-(1-cyano-cyclopentyl)phenyl]-2-(4-pyridylmethyl)amino-3-pyridine
carboxamide
Molecular Weight: 397.48
SMILES:O=C(NC1=CC=C(C2(C#N)CCCC2)C=C1)C3=CC=CN=C3NCC4=CC=NC=C4
InChI Key: WPEWQEMJFLWMLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI: InChI=1S/C24H23N5O/c25-17-24(11-1-2-12-24)19-5-7-20(8-6-19)29-23(30)21-4-3-13-27-22(21)28-16-18-9-14-26-15-10-18/h3-10,13-15H,1-2,11-12,16H2,(H,27,28)(H,29,30)
Mechanism of Action: Kinase Inhibitor; KDR
Inhibitor; Multi-Kinase Inhibitor
Activity: Treatment of Metastatic Gastric
Carcinoma; Anti-cancer Agents; Angiogenesis Inhibitors
Status: Launched 2014 (China)
Chemical Class: Small-molecules; Nitrile
containing; Pyrimidine containing
Originator: Advenchen
Laboratories (USA)/ Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine Co. Ltd (China)
Apatinib Synthesis
US20040259916A1: It appears to be the industrial process.
Identification:
 |
| 1H NMR (Estimated) for Apatinib |
References:
1. Tian, S.; et al. YN968D1 is a novel and selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase with potent activity in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci 2011, 102(7), 1374-80. (FMO only)
2. Chen, G. Six membered amino-amide derivatives an angiogenisis inhibitors. US20040259916A1
3. Yuan, K.; et al. The salts of n-[4-(1-cyanocyclopentyl)phenyl]-2-(4-pyridyl methyl)amino-3-pyridinecarboxamide. WO2010031266A1
4. Sharma, P. S.; et al. VEGF/VEGFR pathway inhibitors as anti-angiogenic agents: present and future. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2011, 11(5), 624-53. (FMO only)