Eliglustat
[N-[(1R,2R)-1-(2,3-Dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl)-1-hydroxy-3-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-2-propanyl]octanamide]
is a small-molecule, oral and potent inhibitor of the enzyme glucosylceramide
synthase. This glucosylceramide analogue has been developed for the treatment
of Gaucher disease type 1 in adults.
Inhibition of the enzyme glucosylceramide synthase reduces the accumulation of the lipid glucosylceramide in the liver, spleen, bone marrow and other organs [1, 2].
 |
| Eliglustat: 2D and 3D Structure |
Eliglustat is the first oral treatment to be approved for first-line use in patients with Gaucher disease type 1. It received its first global approval in the US on 19 August 2014 for the treatment of Gaucher disease type 1 in treatment-naive and treatment-experienced adult patients.
Gaucher Disease Type 1 and Therapy
Gaucher
disease (GD) type 1 is a rare autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder in
which the lipid glucosylceramide accumulates in Gaucher cells in organs
including the spleen, liver and bone marrow due to insufficient production of
the enzyme glucosylceramidase. This leads to clinical manifestations that
include enlargement of the spleen and liver, skeletal complications, anaemia
and thrombocytopenia.
These
cardinal features of GD have been shown to be responsive to enzyme replacement
therapy (ERT) and substrate synthesis inhibition. Both therapeutic approaches
enhance the clearance of the accumulated substrate glucosylceramide (GL1), by
either restoring enzymatic\hydrolytic activity or reducing the concentration of
substrate precursors to a level within the hydrolytic capacity of the mutant
enzyme (glucocerebrosidase).
Substrate
synthesis inhibition is alternatively referred to as substrate reduction
therapy. This therapeutic option entails the inhibition of glucosylceramide
synthase, a Golgi complex enzyme that catalyzes the formation of
glucosylceramide from ceramide and uridine diphosphate glucose.
Two classes of orally administered glucosylceramide synthase inhibitors have been described; namely, iminosugars and analogs of d-threo-1-phenyl-2-decanoylamino-3-morpholino-propanol (PDMP). Miglustat [N-butyldeoxynojirimycin] an alkylated iminosugar, was the first oral substrate synthesis inhibitor to garner regulatory approval, based on clinical trials in adult patients with GD type 1, the non-neuropathic clinical variant. Eliglustat tartrate, a PDMP analog, is a first of its class to be launched [2].
Two classes of orally administered glucosylceramide synthase inhibitors have been described; namely, iminosugars and analogs of d-threo-1-phenyl-2-decanoylamino-3-morpholino-propanol (PDMP). Miglustat [N-butyldeoxynojirimycin] an alkylated iminosugar, was the first oral substrate synthesis inhibitor to garner regulatory approval, based on clinical trials in adult patients with GD type 1, the non-neuropathic clinical variant. Eliglustat tartrate, a PDMP analog, is a first of its class to be launched [2].
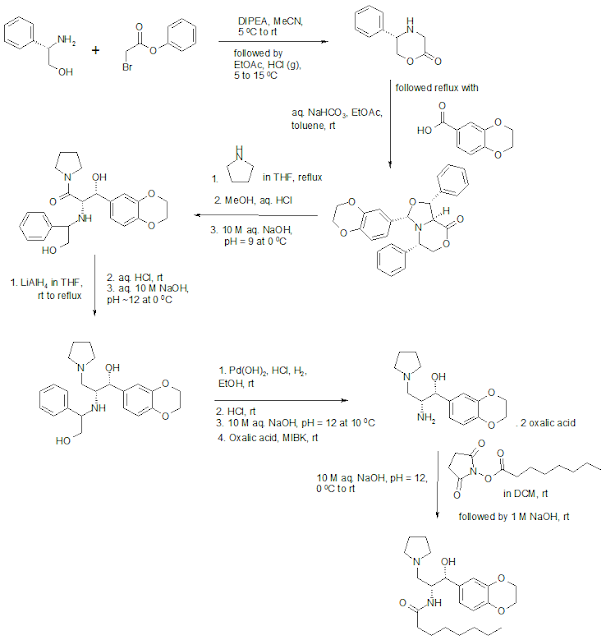
Eliglustat Synthesis
Identifications:
Experimental: 1H NMR
(CDCl3) δ 7.15 (d, J= 8.5Hz,
2H), 6.70 (d, J= 8.5 Hz , 2H), 6.0 (d, J= 7.3, 1H), 4.96 (d, J= 3.8, 1H),
4.3-4.2 ( , 1H), 2.9-2.7 (m, 2H), 2.65-2.55 (m, 4H), 2.10 (t, J= 7.5, 2H), 1.75
(br s, 4H), 1.58- 1.46 ( , 2H), 1.32-1.16 (m, 24H), 0.9 (t, J= 6.7, 3H) ppm.
Sideeffects: The most common
adverse events (AEs) reported by patients (greater than 20%) taking Eliglustat
in clinical trials were fatigue, headache, nausea, diarrhoea, back pain, pain
in the extremities and upper abdominal pain. Most adverse events occurred
within the first 6 months of treatment and only 19 % of adverse events were
considered to be related to the study drug.
Other
adverse events reported included dizziness, asthenia, cough, dyspepsia,
gastroesophageal reflux disease, constipation, palpitations and rash. A total
of 3 %of patients discontinued treatment due to adverse events [1].
References:
1. Poole, R. M. Eliglustat: first global approval. Drugs 2014, 74(15), 1829-1836. (FMO only)
2. Pastores, G. M.; et. al. Eliglustat tartrate: an oral therapeutic option for Gaucher disease type 1. Clin Invest 2014, 4(1), 45-53. (FMO only)
3. Hirth, B. H.; et. al. Synthesis of udp-glucose: n-acylsphingosine glucosyltransferase inhibitors. WO2003008399A1
References:
1. Poole, R. M. Eliglustat: first global approval. Drugs 2014, 74(15), 1829-1836. (FMO only)
2. Pastores, G. M.; et. al. Eliglustat tartrate: an oral therapeutic option for Gaucher disease type 1. Clin Invest 2014, 4(1), 45-53. (FMO only)
3. Hirth, B. H.; et. al. Synthesis of udp-glucose: n-acylsphingosine glucosyltransferase inhibitors. WO2003008399A1